Global Strategy for the Conservation of Brassica Genetic Resources
Global Strategy for the Conservation of Brassica Genetic Resources was published in 2023 (Global Crop Diversity Trust 2023, DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.7544810). This document, developed with the input of a large number of experts, aims to provide a framework for the efficient conservation and effective use of globally important collections of Brassica genetic resources. This webpage provides a summary of some of the its key findings and of the recommendations for priority actions.
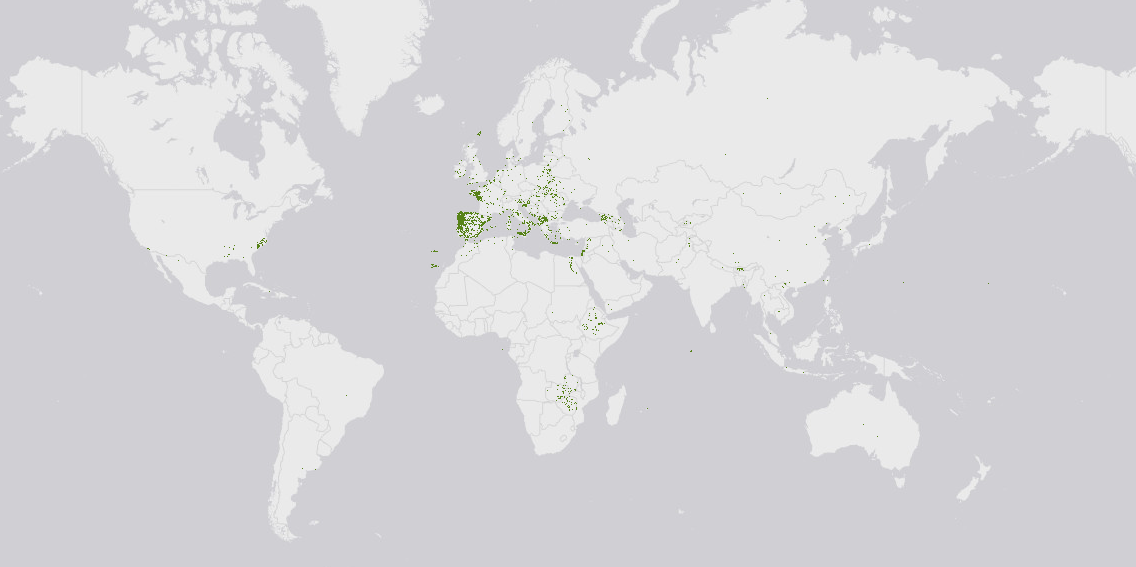
Size of collections and their locations
Data from WIEWS, Genesys indicated a total of over 85,474 Brassica acessions conserved in genebanks at the global level. The interactive bubble map below shows the combined data retrieved in 2023 from Genesys and WIEWS databases.
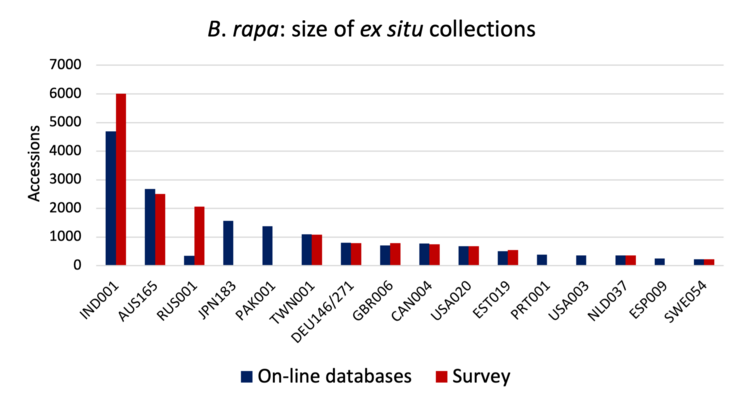
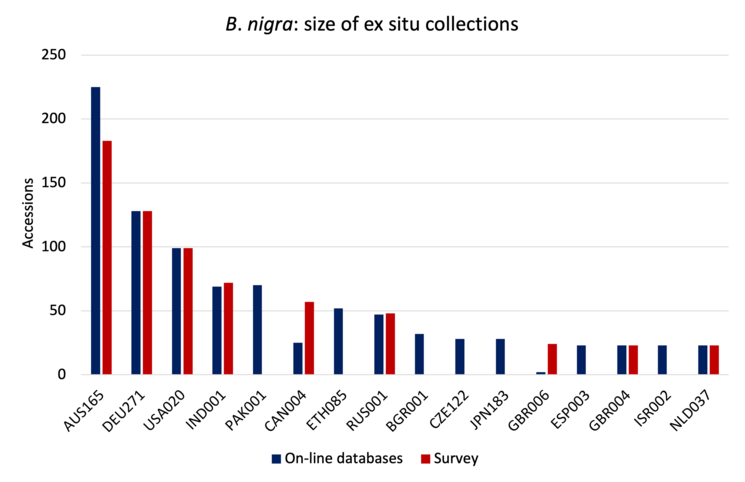
Key collections
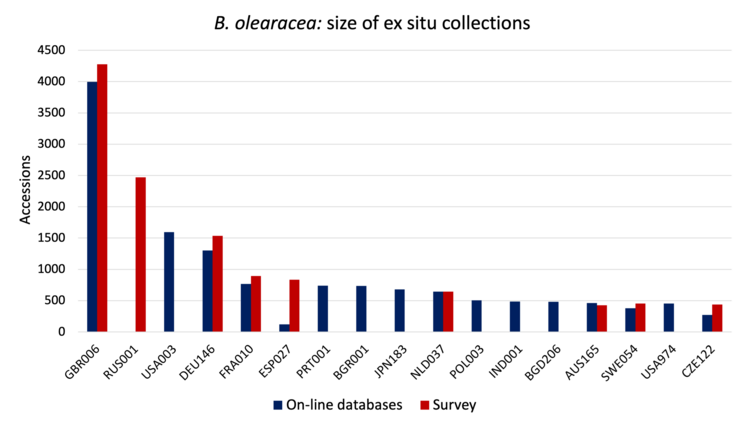
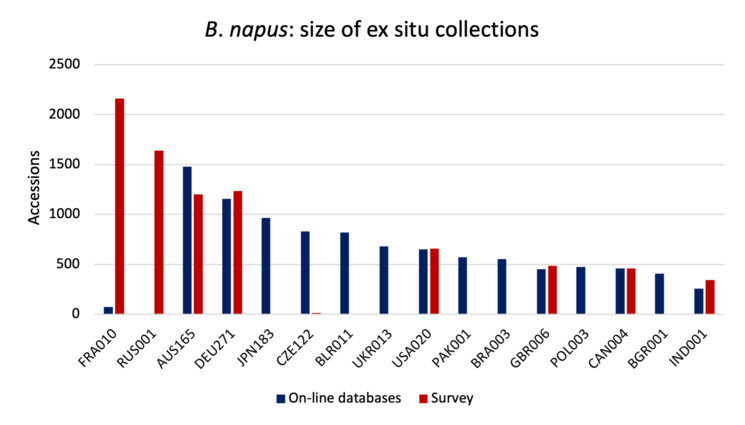
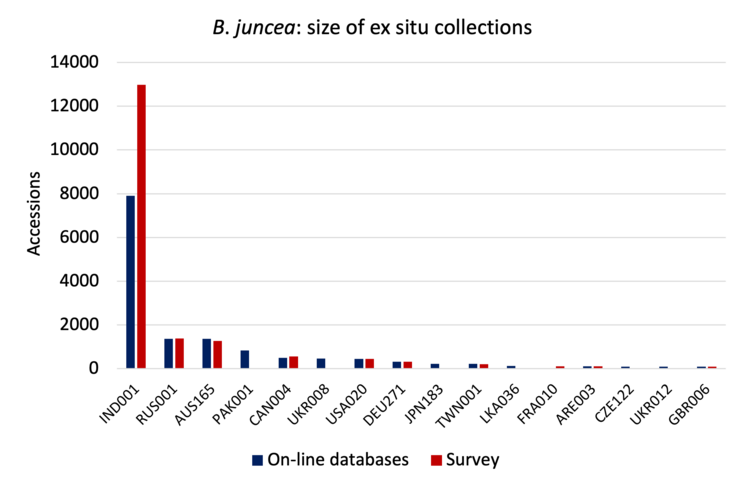
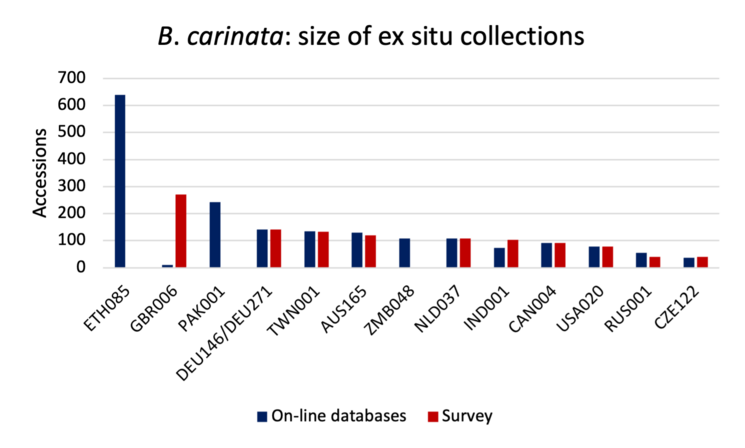
The charts below show the size (number of accessions) of the 16 largest collections of the six main cultivated Brassica species (except for, B. carinata, for which 13 largest collections are shown). Collection holder is identified by the WIEWS institute code, and includes the ISO three letter code for the host country.
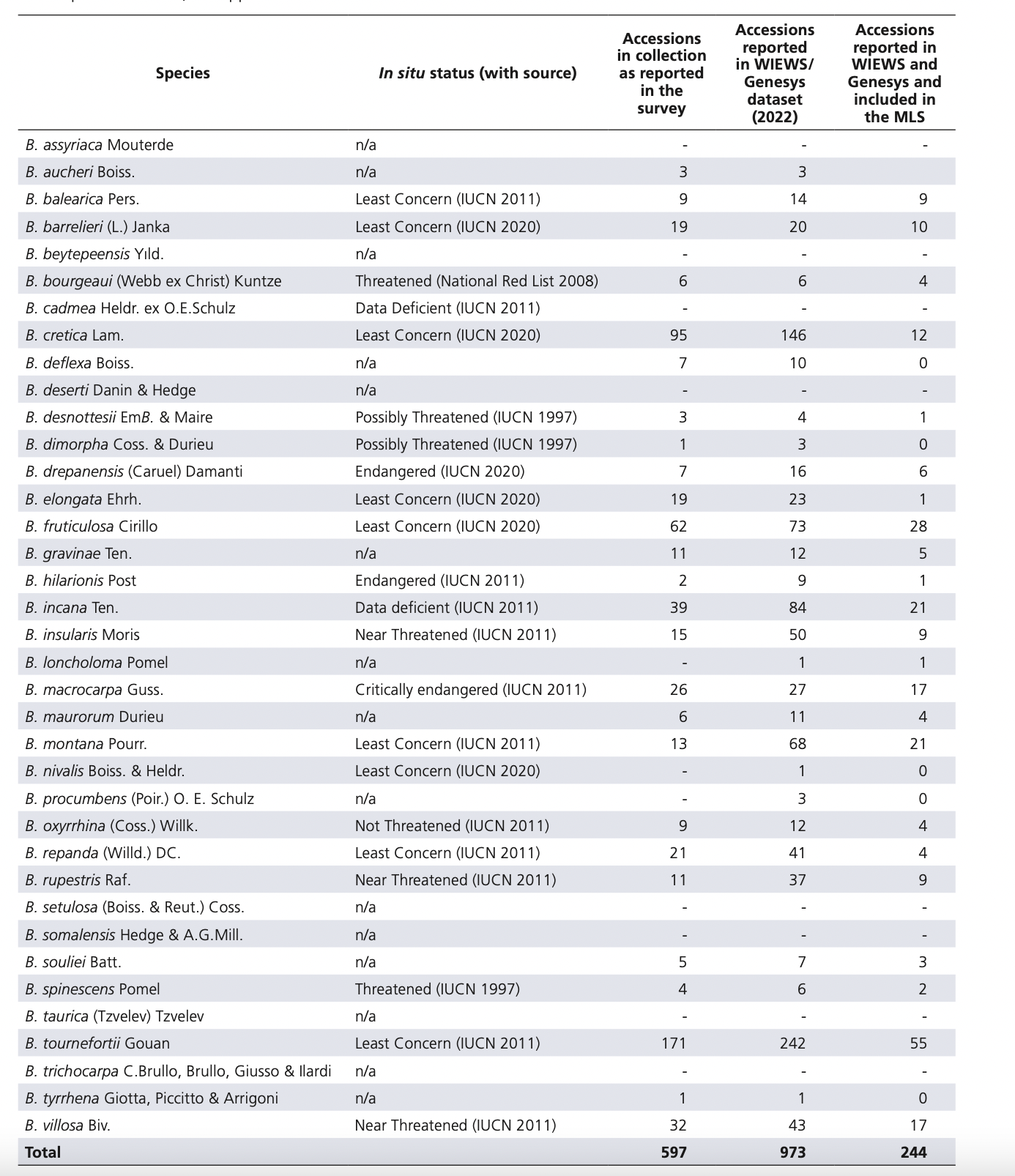
Crop Wild Relatives
The table below shows Brassica CWR IUCN Red List category (IUCN 2011; IUCN 2020) and holdings as reported by 26 collection holders and in the combined WIEWS/Genesys dataset (2022). Taxa reported in Genesys and WIEWS have been standardized and are reported only at the species level. n/a = not applicable
Brassica accessions conserved ex situ by regions where they are stored
The bars show the number of accessions of cultivated and wild Brassica species by regions where they are stored (i.e. the location of the genebanks).
Ex situ holding by biological type
The chart shows the number of Brassica accessions by biological type. For a large proportion of accessions conserved in genebanks the passport data in the open databases do not include information on the biological type of the accessions. The data was retrieved in 2023 from Genesys, WIEWS and GRIN-Global databases.
Brassica diversity tree
A diversity tree is a stratification of a genepool into groups and subgroups. The concept originated in a paper published by van Treuren et al. (2009) proposing a way to analyze and plan the composition of genebank collections. The diversity tree visualization is interactive (click on the tree to open it).
Recommendations for priority actions
- Support for regeneration and long- term storage
- Identification of unique materials for priority conservation
- Documentation – making information available to users and managers
- Crop wild relatives : A gap analysis of global collections for Brassica CWR is essential. Also, understanding which accessions are available for distribution at a global level, and which require regeneration or re-collection, is an essential step to ensure optimal conservation of these species.
- A global Brassica PGR conservation network would offer opportunities for cooperation and improvements to conservation effectiveness and effi- ciency
Partners and donor
The development of this crop conservation strategy was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BMEL) as part of the three-year project led by the Crop Trust: Breathing New Life into the Global Crop Conservation Strategies: Providing an Evidence Base for the Global System of Ex Situ Conservation of Crop Diversity. The Crop Trust also cooperated with the Secretariat of The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (ITPGRFA) in the development of this document.